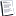 Calculating G
Calculating G
Calculating G
The constant G was anticipated by Newton but first accurately determined in the laboratory by Henry Cavendish in 1798. It has the value G=6.674E-11m3kg−1s−2 (cubic meters per kilogram second squared).
G can be derived from elements of a star by the formula G=gstar*rstar^2/Mstar
gstar rstar Mstar G
Sun 273.97 696,000,000 1.99E+30 6.674E-11
ACa 200.18 853,992,000 2.19E+30 6.674E-11
ACb 332.10 602,040,000 1.80E+30 6.674E-11
AC c 1695.00 98,136,000 2.45E+29 6.674E-11
gstar = surface acceleration in m/sec
rstar = radius in m
Mstar = mass in kg
G can also be derived from g, radius and mass of the planets by the formula
G=gpl*rpl^2/mpl
gpl rpl(m) mpl G
MER 3.71 2,439,000 3.30E+23 6.674E-11
VEN 8.87 6,051,602 4.87E+24 6.674E-11
EAR 9.80 6,378,621 5.97E+24 6.674E-11
MAR 3.71 3,397,360 6.42E+23 6.674E-11
JUP 24.79 71,499,344 1.90E+27 6.674E-11
SAT 10.44 60,273,223 5.68E+26 6.674E-11
URA 8.87 25,556,472 8.68E+25 6.674E-11
NEP 11.15 24,765,365 1.02E+26 6.674E-11
PLU 0.62 1,158,753 1.25E+22 6.674E-11
gpl = surface acceleration of a planet
rpl = radius of a planet
mpl = mass of a planet
The calculated G numbers of the Sun, Alpha Centauri A, B and C and nine planets are identical with the Codata value of G=6.674E-11.


|